Medicine case discussion
Online blended bimonthly assignment toward summative assessment for the month of May 2021
Sahithi nalabolu
1) Pulmonology (10 Marks)
A 55 Year Old Female with Shortness of Breath, pedal Edema and Facial Puffiness.
Question 1. What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
Answer:
QUESTION 2: what are the mechanism of action indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the phramacological and nonphramacological interventions used for this patient?
Answer:
QUESTION 3: WHAT COULD BE THE CAUSES OF HER SUDDEN EXACERBATION?
Answer:
QUESTION 4: Could the ATT have affected her symptoms? If so how?
QUESTION 5:. What could be the causes for her electrolyte imbalance?
2) Neurology (10 Marks)
Case 2a
A 40year old male presented with chief complaints of irrelevant talking and decreased food intake since 9days.
1) what is the evolution of the symptomology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
2)what are the mechanism of action, indication, and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and nonpharmacological interventions used for this patient?
3)why have neurological symptoms appeared this time, that were absent during withdrawal earlier ? what could be a possible cause for this time?
4)what is the reason for giving thiamine in this patient?
5)what is the probable cause for kidney injury in this patient?
6)what is the probable cause for the normocytic anaemia?
7)could chronic alcohlism have aggravated the foot ulcer formation ?if yes and why ?
Case 2B
B) Link to patient details:
A 52 year old male came to the hospital 2 days back presenting with slurring of speech and deviation of mouth that lasted for 1 day and resolved on the same day.
NEUROLOGY
1) What is the evolution of the symptomology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patients problem?
2) What are the mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
3) Did the patients history of denovo hypertension contribute to his current condition?
4) Does the patients history of alcoholism make him more susceptible to ischaemic or haemorrhagic stroke?
Case 2c
C) Link to patient details:
A 45 years old female ,house wife by occupation came to opd with chief complaints of palpitations,chest heaviness,pedal edema,chest pain,radiating pain along her left upper limb , generalized body weakness.
Questions:
1Q)What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
2Q) What are the reasons for recurrence of hypokalemia in her? Important risk factors for her hypokalemia?
3) What are the changes seen in ECG in case of hypokalemia and associated symptoms?
A 55year old male patient came to opd with c/o altered sensorium and involuntary movements from 11pm and recurrent episodes of seizures since 5yrs.
Case2D
1Q)Is there any relationship between occurrence of seizure to brain stroke. If yes what is the mechanism behind it?
2Q). In the previous episodes of seizures, patient didn't loose his consciousness but in the recent episode he lost his consciousness what might be the reason?
Case 2E
Questions: 1) What could have been the reason for this patient to develop ataxia in the past 1 year?
2) What was the reason for his IC bleed? Does Alcoholism contribute to bleeding diatheses ?
Case 2F
Questions
1). Does the patient's history of road traffic accident have any role in his present condition?
2) .What are warning signs of CVA?
3.) What is the drug rationale in CVA?
4) . Does alcohol has any role in his attack?
5).Does his lipid profile has any role for his attack??
Case 2G
A 50 year old male with cervical myelopathy presented to hospital with complaints of weakness of all four limbs since 8 PM yesterday.
__*Questions*_
1Q)what is myelopathy hand?
1 ans)There is loss of power of adduction and extension of the ulnar two or three fingers and an inability to grip and release rapidly with these fingers. These changes have been termed "myelopathy hand" and appear to be due to pyramidal tract involvement.
2Q) what is finger escape?
2ans)Involuntary abduction of fifth finger caused due to unopposed action of extensor digiti MINIMI-WARTENBERG'S SIGN
Presence of weak finger adduction in cervical myelopathy is called - FINGER ESCAPE SIGN
3Q) What is Hoffman's reflex?
3ans)HOFFMANS REFLEX:It is reflectory reaction of muscles after electrical stimulation of type 1a sensory fibres(primary afferent fibres which constantly monitor the how fast a muscle stretch CHANGES) in their innervation nerves
H-REFLEX- is expression of of monosynaptic reflex, which runs in afferents from the muscle and back again through efferents of same muscles
Case 2H
A 17 year old female student by occupation presented to causality on 1/5/2021
Questions
1) What can be the cause of her condition ?
2) What are the risk factors for cortical vein thrombosis?
3)There was seizure free period in between but again sudden episode of GTCS why?resolved spontaneously why?
4) What drug was used in suspicion of cortical venous sinus thrombosis?
3.Cardiology (10marks)
Case 3a
A 78 year old male with shortness of breath, chest pain , bilateral pedal edema and facial puffiness.
1.What is the difference btw heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and with reduced ejection fraction?
2.Why haven't we done pericardiocenetis in this pateint?
3.What are the risk factors for development of heart failure in the patient?
4.)What could be the cause for hypotension in this
Case 3b
A 73 year old male patient with pedal edema, shortness of breath and decreased output.
1Q) .What are the possible causes for heart failure in this patient?
2Q)what is the reason for anaemia in this case?
3Q).What is the reason for blebs and non healing ulcer in the legs of this patient?
There are 4 stages in type 2 diabetes- insulin resistance, prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and type 2 diabetes and vascular complications, including retinopathy, nephropathy or neuropathy and, or, related microvascular events.
The patient is diagnosed with diabetic triopathy exhibiting sequence of neuropathy, retinopathy and nephropathy
The patient has been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy, CKD stage IV and shows signs of diabetic neuropathy such as numbness.
Case 3C
A 52yr old male came to the OPD with the chief complaints of decreased urine output and shortness of breath at rest since one day.
1) What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
2) What are mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
3) What is the pathogenesis of renal involvement due to heart failure (cardio renal syndrome)? Which type of cardio renal syndrome is this patient?
4) What are the risk factors for atherosclerosis in this patient?
5) Why was the patient asked to get those APTT, INR tests for review?
Case3D
67 year old patient with acute coronary syndrome
Questions:
1) What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
2) What are mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
3) What are the indications and contraindications for PCI?
4) What happens if a PCI is performed in a patient who does not need it? What are the harms of overtreatment and why is research on overtesting and overtreatment important to current healthcare systems?
Case 2E
A 60year old Male patient, resident of xxxxxxxx, came to the OPD with the Chief complaint of chest pain since 3 days and giddiness and profuse sweating since morning
1) What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
2) What are mechanism of action, indication and efficacy over placebo of each of the pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions used for this patient?
3) Did the secondary PTCA do any good to the patient or was it unnecessary?
Case 3F
Questions:
1. How did the patient get relieved from his shortness of breath after i.v fluids administration by rural medical practitioner?
2. What is the rationale of using torsemide in this patient?
3. Was the rationale for administration of ceftriaxone? Was it prophylactic or for the treatment of UTI?
4) Gastroenterology (& Pulmonology) 10 Marks
Case 4a
A 33 year old man with pancreatitis, pseudocyst and left broncho-pleural fistula
QUESTIONS:
1) What is the evolution of the symptomatology in this patient in terms of an event timeline and where is the anatomical localization for the problem and what is the primary etiology of the patient's problem?
2) What is the efficacy of drugs used along with other non pharmacological treatment modalities and how would you approach this patient as a treating physician?
Case 4B
Case discussion on 25 yr old male with epigastric pain
1) What is causing the patient's dyspnea? How is it related to pancreatitis?
2) Name possible reasons why the patient has developed a state of hyperglycemia?
3) What is the reason for his elevated LFTs? Is there a specific marker for Alcoholic Fatty Liver disease?
4) What is the line of treatment in this patient?
Case 4c
A 45 year old Female patient with Fever, Pain abdomen, Decreased Urine output and Abdominal distension
1) What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
Ans)Differential Diagnosis:
· *Ruptured
Liver Abscess.
· *Organized
collection secondary to Hollow viscous Perforation.
· * Organized
Intraperitoneal Hematoma.
· * Free
fluid with internal echoes in Bilateral in the Subdiaphragmatic space.
· * Grade
3 RPD of right Kidney
*The most probably diagnosis is there is
abdominal hemorrhage. This will give reasoning to the abdominal distention, and
the blood which is aspirated.
2) What was the cause of her death?
Ans)After leaving the hospital, the patient went
to Hyderabad and underwent an emergency laparotomy surgery. The patient passed
away the next day. Cause of her death can be due to complications of laparotomy
surgery such as, hemorrhage (bleeding), infection, or damage to internal organs.
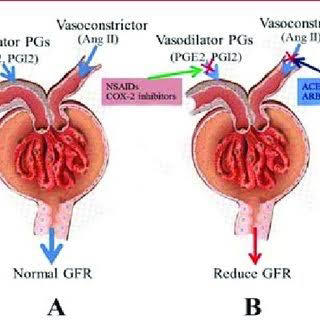
3) Does her NSAID abuse have something to do with her condition? How?
Ans)NSAID-induced renal dysfunction has a wide spectrum of negative effects, including decreased glomerular perfusion, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and acute renal failure. *Chronic NSAIDs use has also been related to hepatotoxicity. While the major adverse effects of NSAIDs such as gastrointestinal mucosa injury are well known, NSAIDs have also been associated with hepatic side effects ranging from asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and hepatitis with jaundice to fulminant liver failure and death.
case 5A
Post TURP with non oliguric ATN
A 52 yr old male patient who is a farmer by occupation
Presented to hospital on 17 May 2021 with Chief Complaints of
- SOB since 4 days
- Burning micturition since 4 days
- Fever since 2 days
Link to patient details:
1.what could be the cause for his SOB?
2. Reason for Intermittent Episodes of drowsiness?
3.why did he complaint of fleshy mass like passage in urine?
4. What are the complications of TURP that he may have had?
case 5B
An Eight year old with Frequent Urination
2. Why doesn't the child have the excessive urge of urination at night time ?
6) Infectious Disease (HI virus, Mycobacteria, Gastroenterology, Pulmonology) 10 Marks
Case 6A
A) Link to patient details
QUESTION 1:
1.Which clinical history and physical findings are characteristic of tracheo esophageal fistula?
ANSWER: Cough since 2 months on taking food and liquids
•difficulty in swallowing since 2 month . It was initially difficult only with solids but then followed by liquids also.
*laryngeal crepitus- positive
*These favour for tracheo esophageal.fistula
2) What are the chances of this patient developing immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome? Can we prevent it?
*ANSWER: Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) represents the worsening of a recognized (paradoxical IRIS) or unrecognized (unmasking IRIS) pre-existing infection in the setting of improved immunologic function.
*The most effective prevention of IRIS would involve initiation of ART before the development of advanced immunosuppression. IRIS is uncommon in individuals who initiate antiretroviral treatment with a CD4+ T-cell count greater than 100 cells/uL.
*Aggressive efforts should be made to detect asymptomatic mycobacterial or cryptococcal disease prior to the initiation of ART, especially in areas endemic for these pathogens and with CD4 T-cell counts less than 100 cells/uL.
*Two prospective randomized studies are evaluating prednisone and meloxicam for the prevention of paradoxical TB IRIS.
7) Infectious disease and Hepatology:
A 55 year old male patient who is a palm tree climber by Occupation
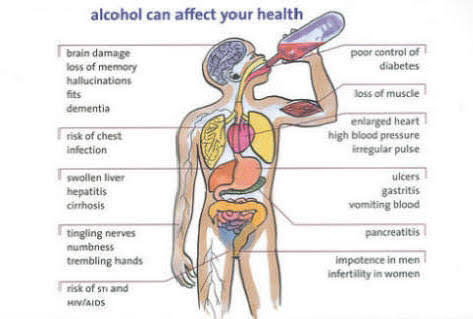
2. What is the etiopathogenesis of liver abscess in a chronic alcoholic patient ? ( since 30 years - 1 bottle per day)
3. Is liver abscess more common in right lobe ?
4.What are the indications for ultrasound guided aspiration of liver abscess ?
Question-1:
Cause of liver abcess in this patient ?
Answer:
Here ; the cause of liver abcess is :
* Amoebic liver abcess (ALA ) seen commonly in the tropics is predominantly confined to adult males, especially those who consume locally brewed alcohol, although intestinal amoebiasis occurs in all age groups and in both genders
It has been argued that socioeconomic factors and poor sanitary conditions are the primary culprits that casually link alcohol to ALA.
* However , there has emerged an abundance of data that implicates alcohol in a more causal role in facilitating the extraintestinal invasion of the infective protozoan and the subsequent development of ALA.
## Hence the consumption of locally made alcohol ( toddy ) is the most likely cause of Liver abcess in this patient.
Question-2:
How do you approach this patient ?
Answer:
Question-3:
Why do we treat here ; both amoebic and pyogenic liver abscess?
Answer:
* Considering the following factors:
1) Age and gender of patient: 21 years ( young ) and male.
2) Single abcess.
3) Right lobe involvement.
## The abcess is most likely AMOEBIC LIVER ABSCESS …
** But most of the patients with amoebic liver abcess have no bowel symptoms, examination of stool for ova and parasite and antigen testing is insensitive and insensitive and not recommended.
# And considering the risk factors associated with aspiration for pus culture:
1) Sometimes ; abcess is not accessible for aspiration if it is in posterior aspect or so.
2) Sometimes ; it has thin thinwall which may rupture if u aspirate.
3) Sometimes ; it is unliquefied.
## There how can u confirm whether it is pyogenic/ amoebic , so we treat them both empirically in clinical practice.
Question-4:
Is there a way to confirmthe definitive diagnosis in this patient?
Answer:
There is no way to confirm the definitive diagnosis…(as mentioned above)





































Comments
Post a Comment